Unlock the Code: How Two Numbers Create the Digital World!
(Math Helps You Become a Tech Superhero!)

The Binary System: The Secret Language of Computers
When you look at your computer screen, a YouTube video, or a movie on TV, you see an image so vivid and colorful it seems almost magical. But beneath that digital surface, everything is built from the simplest duo you can imagine: the numbers 0 and 1.
This is the Binary System, the secret language of computers.
Think of a light switch: It's either OFF (0) or ON (1). There's nothing in between. Computers use billions of these tiny 'switches' (transistors) to think, remember, and interact with the world. Each 0 or 1 is called a bit.
Why Do Computers Use Only Two Numbers?
We use the decimal system (base 10), probably because we have ten fingers. It's familiar and easy for us to calculate with.
But for electronic machines, it's much easier and more reliable to understand if an electric current is simply flowing (1) or not flowing (0). Imagine trying to build a tiny switch that could reliably recognize ten different levels of 'on' – it would be a nightmare! Simplicity is the key to speed and accuracy in computers.

The 'Power' of Exponents: Math You Already Know!
Remember place value in math? In the number 345:
• the 5 is in the units place 5 x 100 = 5 x 1 = 5 • the 4 is in the tens place 4 x 101 = 4 x 10 = 40 • the 3 is in the hundreds place 3 x 102 = 3 x 100 = 300 (Total= 300 + 40 + 5 = 345)
The binary system uses the exact same idea, but with powers of 2 instead of 10!
Let's decode the binary number 1101:
• The rightmost digit is 1 and corresponds to: 1 x 20 = 1 x 1 = 1 • The next digit is 0 which corresponds to: 0 x 21= 0 x 2 = 0 • The next 1: 1 x 22 = 1 x 4 = 4 • The leftmost 1: 1 x 23= 1 x 8 = 8 Add them up: 8 + 4 + 0 + 1 = 13. So, binary 1101 is just the number 13 in disguise!

The Importance of Bits: What Can You Do with 0 and 1?
Why is this 'power' important? The number of bits (those 0s or 1s) tells us how many different things we can represent.
• 1 bit has 21= 2 possibilities (0, 1) • 2 bits have 22= 4 possibilities (00, 01, 10, 11) • 3 bits (23) have 8 possibilities (000, 001, ..., 111) • ...and we get to... • 8 bits (one "byte") have 28= 256 possibilities!
256 possibilities from just eight 0s and 1s! That's enough to represent every letter (A-Z, a-z), every number (0-9), all punctuation marks, and still have codes left over! This is the magic of exponents in action!

From Binary Bits to Screens: Painting with Numbers!
So how does the binary system turn into the stunning graphics on your screen?
- The Magic of Pixels: Your screen is made of millions of tiny dots called pixels. Each pixel is like a tiny, programmable light.
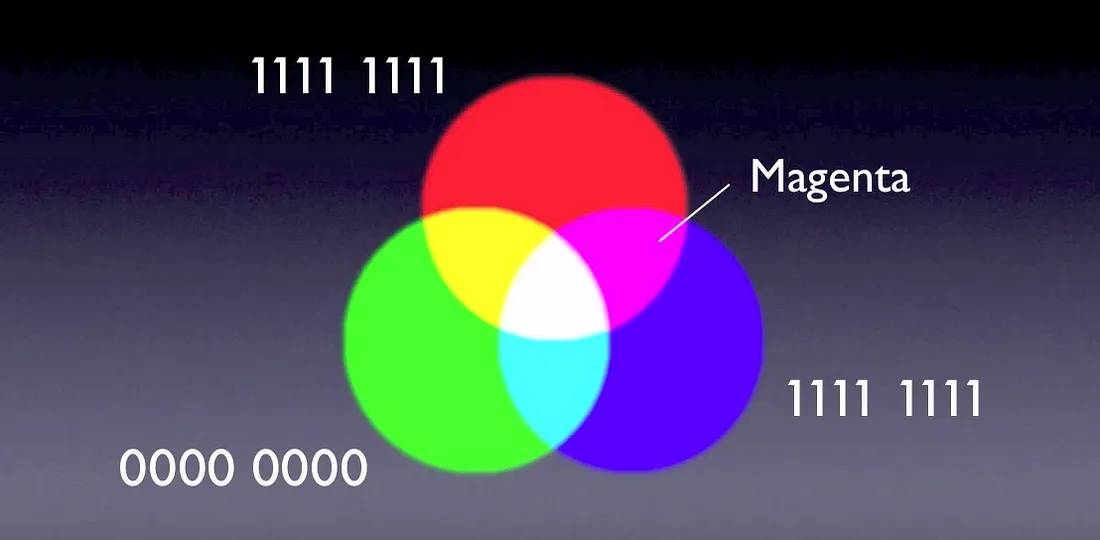
- The Color Code (RGB): Each pixel usually has three even smaller lights: Red, Green, and Blue. By changing the brightness of each of these three, a pixel can display almost any color.
- Binary Signal for Brightness: How do we tell a tiny red light how bright to be? With the binary system, of course! Often, each color (Red, Green, Blue) gets 8 bits of information. • 00000000 (binary for 0) could mean the color is completely OFF. • 11111111 (binary for 255) could mean the color is at FULL BRIGHTNESS. • Any 8-bit number in between (e.g., 10000000 for medium brightness) gives a different shade!
- Since each of the R, G, and B can have 28 = 256 levels of brightness, the total number of colors a pixel can display is 256 x 256 x 256 = 16,777,216 colors! This is 'True Color', all from strings of 0s and 1s, powered by the mathematics of exponents!
- The GPU: Your Computer's Super-Fast Artist: Your computer's Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a mathematical beast! It takes all these binary codes for millions of pixels and tells each one what color to be, updating them many, many times every second. That's how you get smooth videos and fast games!
The Binary System: Your Computer's Universal Language
This isn't just about screens!
- You type a letter? Your keyboard sends a unique binary code for that letter.
- You click your mouse? Binary signals say 'button pressed' or 'button released'.
- You listen to music? The digital music file is a long series of binary digits, which is turned back into sound waves by a chip doing (you guessed it) math!
- Everything your computer does, every app, every website, every game, is ultimately a dance of 0s and 1s, interpreted using the rules of mathematics you are learning right now.
Next Time in Math Class...
Remember, you're not just learning about exponents, place value, or logic. You are learning the fundamental building blocks of the entire digital world! You are learning to speak the language of technology.
That's why mathematics isn't just a subject. It gives you the ability to understand, create, and innovate in a world increasingly shaped by 0s and 1s.
Want to unlock more digital secrets and see how your math skills can become your greatest advantage? Explore this amazing world with us at Kosmosmath!